Introduction
What is RRTS project? Indian government is going to introduce fastest train in the country known as RRTS i.e Regional Rapid Transit System. The RRTS is a dedicated, fast and high capacity rail based commuter service that will connect major cities of Haryana, Rajasthan and UP to Delhi.
Delhi is changing in terms of mobility. The regional transport system, or RRTS, is anticipated to be a major factor in improving Delhi’s transit system, which is currently comparatively superior. Prime Minister Narendra Modi opened the Uttar Pradesh-based Sahibabad RapidX Station earlier this year.Following the opening, Prime Minister Modi also turned on the RapidX train that runs from Sahibabad to the Duhai depot. All of this is a part of the nation’s first semi-high-speed regional rail system, called the Regional Rapid Transit System, or RRTS.
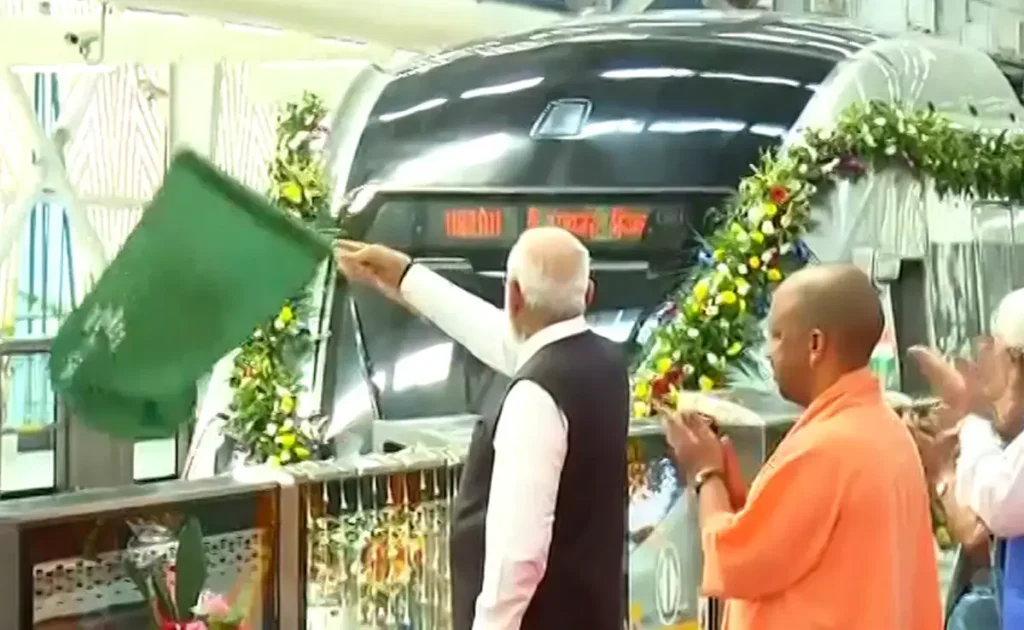

‘NaMo Bharat’ will be the name of the trains of the Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS), which Prime Minister Narendra Modi unveiled , according to Union Minister Hardeep Singh Puri.In April, the National Capital Region Transport Corporation (NCRTC), which is implementing India’s first semi-high-speed regional rail service project, had named RRTS trains as ‘RAPIDX’.

Why is India investing in the RRTS project?
India is investing in the Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS) project for several reasons. Here are some of the key factors that have led to the development of the project:
- Growing Population and Urbanization: The population of the National Capital Region (NCR) has been growing rapidly, and is projected to reach 64 million by 2031. This has led to increased demand for transportation services, especially for faster and more efficient connectivity between different cities and suburbs in the region.
- Traffic Congestion and Air Pollution: The NCR suffers from severe traffic congestion and air pollution, which have a negative impact on the health and well-being of its residents. The RRTS project aims to address these issues by providing a reliable and efficient alternative to private vehicles.
- Economic Growth: The NCR is an important economic hub that generates significant employment opportunities and contributes to India’s GDP. The RRTS project is expected to boost economic growth by improving connectivity and making it easier for people to access job opportunities and other services in different parts of the region.
- International Best Practices: The RRTS project draws on international best practices in high-speed rail technology and is aligned with the Indian government’s vision of modernizing the country’s infrastructure.
- Sustainable Development: The RRTS project is part of India’s commitment to sustainable development and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By promoting public transportation and reducing reliance on private vehicles, the project aims to improve the overall quality of life in the region.
In summary, India is investing in the RRTS project to address the transportation needs of a rapidly growing population, reduce traffic congestion and air pollution, boost economic growth, adopt international best practices, and promote sustainable development.
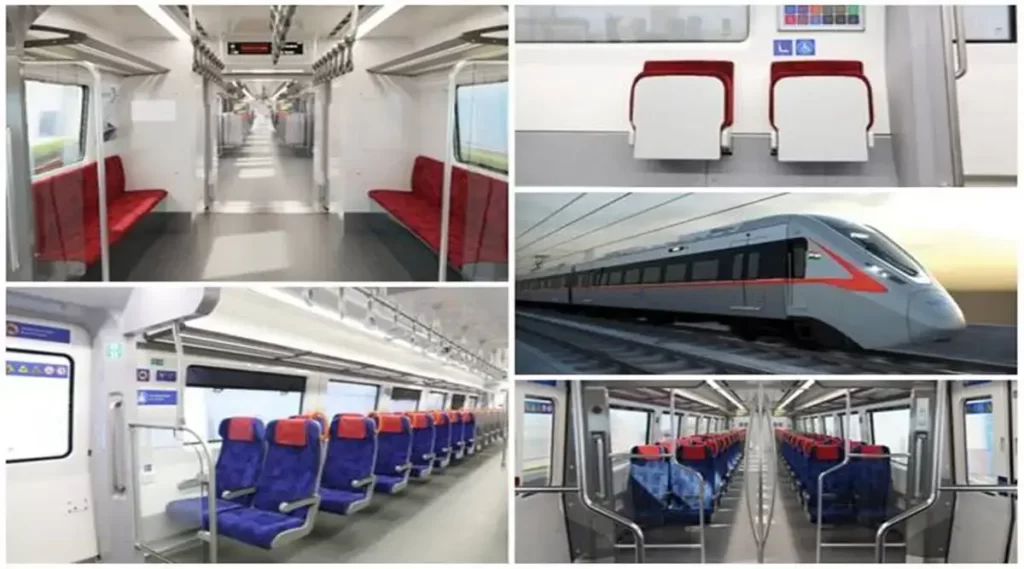

Understanding the Benefits of the RRTS Project
The Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS) project is a transformative initiative that aims to bring about a paradigm shift in India’s transportation infrastructure. This ambitious project has been launched with the aim of providing world-class, high-speed commuter train services to the National Capital Region (NCR) and beyond. Here are some of the benefits of the RRTS project:
- Faster Commute Times: The RRTS will significantly reduce travel time between cities by providing high-speed, express train services. For example, the Delhi-Meerut RRTS corridor is expected to reduce travel time between the two cities from 3-4 hours to just 60 minutes.
- Reduced Congestion: The RRTS project aims to provide an alternative to private vehicles and reduce traffic congestion on roads, which is a major problem in the NCR. By offering fast, reliable and comfortable transit options, the RRTS will encourage more people to switch from private vehicles to public transportation.
- Environmentally Sustainable: The RRTS project is a step towards environmentally sustainable transportation. By promoting public transportation, the project aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality in the NCR.
- Improved Connectivity: The RRTS corridors will improve connectivity between cities, towns and suburbs in the NCR. This will make it easier for people to access job opportunities and other services in different parts of the region.
- Boost to Local Economy: The RRTS project is expected to generate significant economic benefits by creating employment opportunities, boosting tourism and promoting commercial activity along the corridors.
Overall, the RRTS project is a transformative initiative that has the potential to change the way people travel in the NCR. By providing fast, reliable and environmentally sustainable transit options, the project will benefit commuters, businesses and the environment.
Also Read : What is Sir Creek Line? | Why it is still debatable between India and Pakistan?
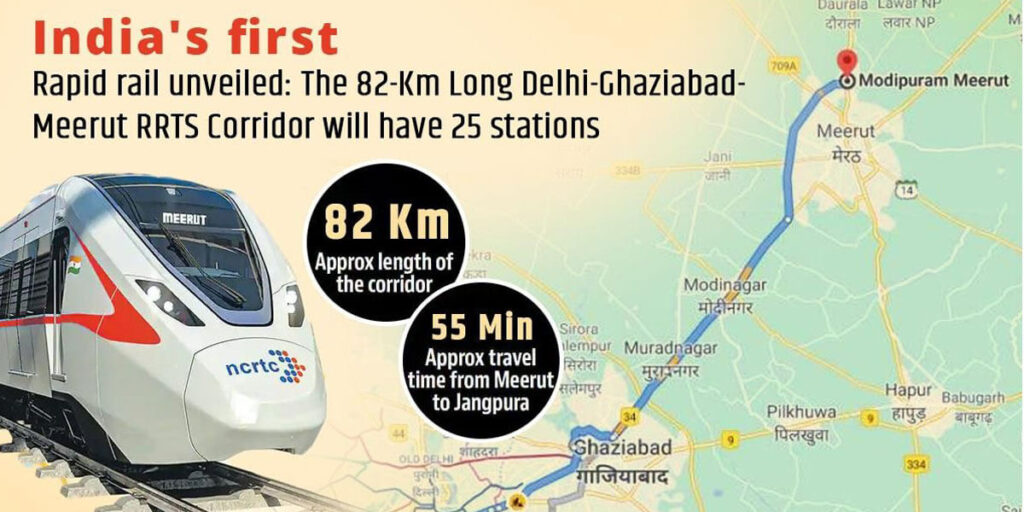
RRTS Corridors and Their Impact on Cities
The Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS) project in India comprises several corridors that are expected to have a significant impact on the cities they serve. Here is an overview of the RRTS corridors and their impact on cities:
- Delhi-Meerut RRTS Corridor: This corridor covers a distance of around 82 km and connects Delhi with Meerut. It is expected to significantly reduce travel time between the two cities, from around 3-4 hours by road to just 60 minutes by RRTS. The corridor is also expected to boost economic growth in the region, by improving connectivity and accessibility to job opportunities.
- Delhi-Ghaziabad-Meerut RRTS Corridor: This corridor covers a distance of around 92 km and connects Delhi with Meerut via Ghaziabad. It is expected to reduce travel time between Delhi and Meerut to just 55 minutes by RRTS, and between Delhi and Ghaziabad to just 25 minutes. The corridor is expected to boost economic growth in the region, by improving connectivity and accessibility to job opportunities.
- Delhi-Panipat RRTS Corridor: This corridor covers a distance of around 111 km and connects Delhi with Panipat. It is expected to reduce travel time between the two cities to just 50 minutes by RRTS. The corridor is expected to boost economic growth in the region, by improving connectivity and accessibility to job opportunities.
- Delhi-Alwar RRTS Corridor: This corridor covers a distance of around 164 km and connects Delhi with Alwar in Rajasthan. It is expected to significantly reduce travel time between the two cities, from around 4-5 hours by road to just 120 minutes by RRTS. The corridor is also expected to boost economic growth in the region, by improving connectivity and accessibility to job opportunities.
- Delhi-Mathura-Vrindavan RRTS Corridor: This corridor covers a distance of around 141 km and connects Delhi with Mathura and Vrindavan. It is expected to significantly reduce travel time between the cities, from around 3-4 hours by road to just 90 minutes by RRTS. The corridor is also expected to boost tourism in the region, by improving accessibility to popular religious sites.
- Delhi-Gurugram-SNB RRTS Corridor: This corridor covers a distance of around 106 km and connects Delhi with Gurugram and SNB (Shahjahanpur-Neemrana-Behror). It is expected to reduce travel time between Delhi and Gurugram to just 50 minutes by RRTS. The corridor is expected to boost economic growth in the region, by improving connectivity and accessibility to job opportunities.
- Delhi-Sonipat-Panipat RRTS Corridor: This corridor covers a distance of around 103 km and connects Delhi with Sonipat and Panipat. It is expected to reduce travel time between Delhi and Panipat to just 50 minutes by RRTS. The corridor is expected to boost economic growth in the region, by improving connectivity and accessibility to job opportunities.
Overall, the RRTS corridors are expected to significantly improve transportation connectivity and accessibility in the National Capital Region, by reducing travel time and improving accessibility to job opportunities and tourism sites. The corridors are also expected to boost economic growth in the region, by improving accessibility to markets and job opportunities.

Financing and Timeline of the RRTS Project
The Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS) project is a major initiative that requires significant financial investment and long-term planning. Here is an overview of the financing and timeline of the project:
Financing:
The RRTS project is being implemented through a partnership between the central government and the state governments of Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, and Haryana. The central government is providing the majority of the funding for the project, with a contribution of around 50% of the total cost. The remaining funding is being provided by the state governments and through loans from international organizations such as the World Bank and the Asian Development Bank.
Timeline:
The RRTS project is being implemented in three phases, with a total of eight corridors planned for construction. Here is an overview of the timelines for each phase:
Phase 1:
The first phase of the project comprises three corridors – Delhi-Meerut, Delhi-Ghaziabad-Meerut, and Delhi-Panipat – covering a total length of around 364 km. The construction of these corridors began in 2019, and they are expected to be completed by 2025.
Phase 2:
The second phase of the project comprises five corridors – Delhi-Alwar, Delhi-Panipat, Delhi-Mathura-Vrindavan, Delhi-Gurugram-SNB (Shahjahanpur-Neemrana-Behror) and Delhi-Sonipat-Panipat – covering a total length of around 581 km. The construction of these corridors is expected to begin in 2023 and be completed by 2028.
Phase 3:
The third phase of the project comprises three corridors – Delhi-Meerut 2, Delhi-Haridwar, and Delhi-Rohtak – covering a total length of around 296 km. The construction of these corridors is expected to begin in 2025 and be completed by 2030.
Overall, the RRTS project is a long-term initiative that is expected to take several years to complete. The project is being implemented in a phased manner, with construction work currently underway on the first phase corridors. Once completed, the RRTS project is expected to significantly improve transportation connectivity and boost economic growth in the National Capital Region.

Challenges in Implementing the RRTS Project
The Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS) project is a complex initiative that involves several challenges in its implementation. Here are some of the key challenges faced in implementing the RRTS project:
- Land Acquisition: One of the major challenges faced in implementing the RRTS project is land acquisition. The project requires a large amount of land for construction, which often involves acquiring land from private owners, farmers, and other stakeholders. The process of land acquisition can be time-consuming and contentious, leading to delays and increased costs.
- Environmental Concerns: The RRTS project requires the construction of elevated tracks, stations, and other infrastructure that can have a negative impact on the environment. The project may lead to deforestation, loss of wildlife habitat, and increased air and noise pollution. It is important to ensure that environmental concerns are adequately addressed through proper planning, mitigation measures, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Technical Complexity: The RRTS project involves complex engineering and technical requirements, including high-speed trains, advanced signaling systems, and sophisticated infrastructure. Implementing these technical requirements requires specialized skills and expertise, which may be in short supply. Ensuring the availability of skilled labor and technical expertise is essential to the successful implementation of the project.
- Coordination with Stakeholders: The RRTS project involves multiple stakeholders, including central and state governments, local authorities, private landowners, and affected communities. Ensuring effective coordination and communication with these stakeholders is essential to the successful implementation of the project. It is important to address their concerns, involve them in decision-making, and ensure their participation in the project.
- Funding: The RRTS project requires significant financial investment, and securing funding can be a major challenge. The project is being implemented through a partnership between the central and state governments, as well as loans from international organizations. Ensuring adequate and timely funding is critical to the successful implementation of the project.
The RRTS project faces several challenges in its implementation, including land acquisition, environmental concerns, technical complexity, coordination with stakeholders, and funding. Addressing these challenges effectively is essential to the successful implementation of the project and achieving its intended benefits.

Conclusion: A Step Forward for India’s Transportation System
In conclusion, the RRTS project is a game-changing initiative that aims to revolutionize the way people travel in India’s National Capital Region. The project is designed to provide a fast, safe, and comfortable mode of transportation for commuters, which will help reduce traffic congestion and air pollution. With the implementation of this project, the government hopes to boost economic growth and improve the quality of life for residents in the region. The RRTS project is a step in the right direction towards achieving sustainable urban development and creating a better future for generations to come.

1 thought on “What is RRTS Project, RapidX and Namo Bharat? Know Everything About Fastest Train in India”